How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, whether for professional videography, aerial photography, or recreational purposes. This guide provides a structured approach to mastering drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and safety regulations. We’ll explore the intricacies of various drone components, helping you understand their functions and how they contribute to a successful flight.
From understanding your drone’s battery life to navigating complex flight paths, we aim to equip you with the knowledge necessary to confidently take to the skies.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the specifics of drone technology, including different camera types, battery specifications, and the functionalities of various flight modes. We will also address crucial safety protocols and legal considerations, ensuring that your drone operations remain compliant and responsible. By the end, you’ll be well-prepared to navigate the exciting world of drone piloting.
Drone Components and Their Functions
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight and functionality. This section details the key components and their respective functions, along with comparisons of different types.
Drone Component Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the integrated work of several key components. Let’s explore each one individually.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to lift off, move, and hover. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into rotational motion. Brushless motors are commonly used in modern drones for their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: This is the drone’s “brain,” processing data from various sensors and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands from the transmitter. It’s responsible for orientation, stabilization, and flight mode selection.
- Battery: The battery provides power to all the drone’s components. LiPo (Lithium Polymer) batteries are standard, offering high energy density but requiring careful handling and storage.
- Camera: This captures photos and videos. The type and quality of the camera vary greatly depending on the drone model and intended use.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): This allows the drone to determine its location, aiding in navigation, autonomous flight modes (like Return-to-Home), and geofencing.
- Transmitter: This is the remote control used to pilot the drone, sending commands to the flight controller.
Drone Camera Types and Applications
Drone cameras come in a variety of types, each suited to different needs. The choice depends on factors like resolution, image quality, and desired features.
- Standard Cameras: Offer good image quality for general purposes, suitable for recreational flying and basic aerial photography.
- High-Resolution Cameras: Capture highly detailed images and videos, ideal for professional photography, mapping, and inspection tasks.
- Thermal Cameras: Detect heat signatures, useful for search and rescue operations, building inspections, and monitoring infrastructure.
- Zoom Cameras: Allow for variable focal lengths, enabling shots from a distance without requiring the drone to move closer to the subject.
Drone Battery Types and Comparison
Different drone batteries offer varying flight times and charging methods. Understanding these differences is essential for planning flights and ensuring sufficient power.
- LiPo Batteries: These are the most common type, offering high energy density but requiring careful handling due to their flammability. Charging times vary depending on the battery capacity and charger.
- LiHV Batteries: These offer higher voltage than standard LiPos, resulting in increased flight time and power.
Drone Model Specifications Comparison
Here’s a comparison of three hypothetical drone models to illustrate the variations in specifications.
| Model | Battery Life (minutes) | Camera Resolution (MP) | Max Flight Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone X | 25 | 12 | 5 |
| Drone Y | 35 | 20 | 7 |
| Drone Z | 20 | 48 | 3 |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is essential to ensure safe and successful operation. This involves several key steps to verify the drone’s functionality and the surrounding environment.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
A systematic pre-flight inspection helps identify potential issues before they lead to problems during the flight. This checklist should be followed religiously.
- Visually inspect the drone for any damage to the propellers, motors, or body.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Confirm that all the drone’s components are securely attached.
- Power on the drone and transmitter, ensuring a stable connection.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Check the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flying.
- Select a safe and legal flight location, considering obstacles and airspace restrictions.
Compass and GPS Calibration, How to operate a drone
Calibrating the drone’s compass and GPS is crucial for accurate navigation and stability. Failure to do so can lead to erratic flight behavior and potential crashes.
The specific calibration procedure varies depending on the drone model, but generally involves slowly rotating the drone horizontally and vertically to allow the sensors to orient themselves.
Safe and Legal Flight Location Selection
Choosing a safe and legal flight location is paramount for responsible drone operation. Factors to consider include airspace restrictions, proximity to people and property, and environmental conditions.
Always check local regulations and obtain necessary permits before flying. Avoid flying near airports, crowds, or sensitive areas.
Flight Path Planning
Planning a flight path beforehand ensures a smoother and safer flight. Consider wind conditions, obstacles, and the desired shots or data collection points.
Visualizing the flight path helps avoid collisions and allows for adjustments based on real-time conditions.
Basic Drone Operation and Controls

Understanding the basic controls of a drone transmitter is the first step to successful operation. This section covers the fundamental techniques for takeoff, hovering, landing, and basic maneuvers.
Transmitter Control Stick Functions
Most drone transmitters have two pairs of control sticks. Each stick controls a specific aspect of the drone’s movement.
- Left Stick (Yaw and Throttle): The left stick typically controls the drone’s altitude (throttle) and yaw (rotation around its vertical axis).
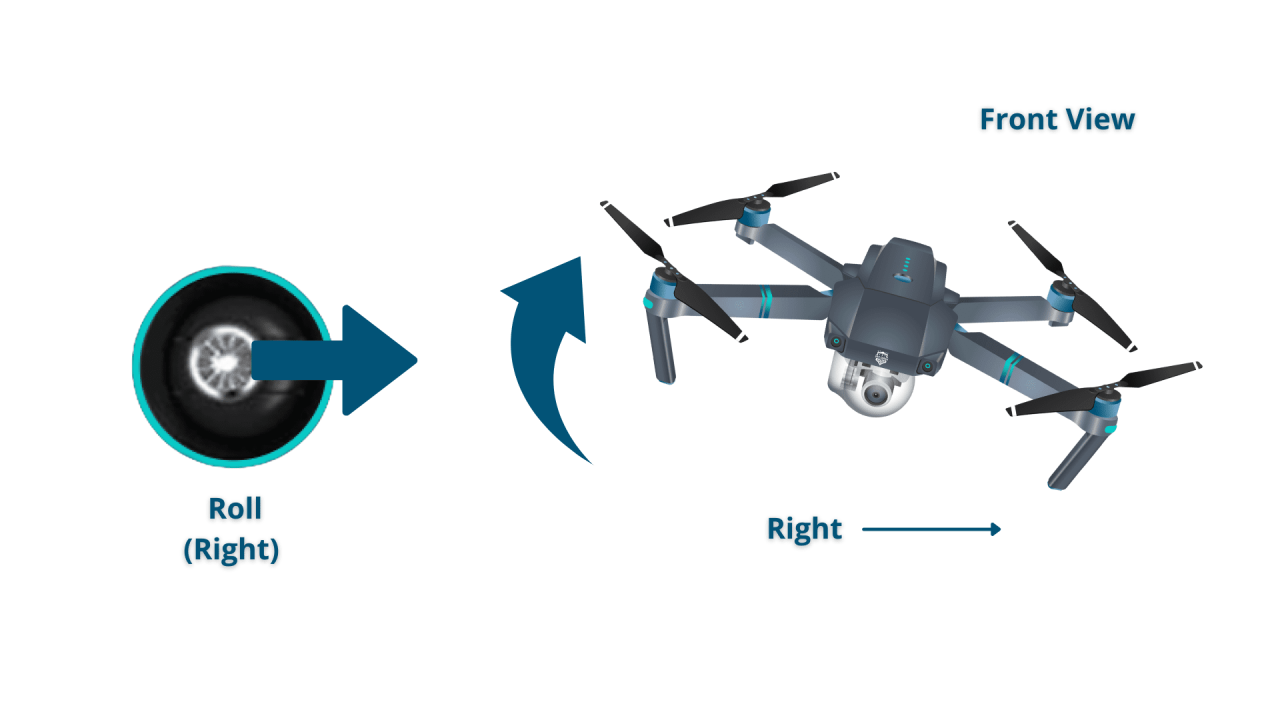
- Right Stick (Pitch and Roll): The right stick controls the drone’s pitch (forward and backward movement) and roll (side-to-side movement).
Takeoff, Hovering, and Landing Techniques
These are fundamental maneuvers that form the basis of all drone operations.
- Takeoff: Gently increase the throttle (left stick upwards) to lift the drone smoothly off the ground.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable altitude and position by carefully adjusting the throttle and control sticks.
- Landing: Gradually decrease the throttle to lower the drone gently to the ground.
Controlling Altitude, Direction, and Speed
Precise control over these aspects is essential for smooth and controlled flight.
- Altitude: Controlled by the throttle (left stick).
- Direction: Controlled primarily by the right stick (pitch and roll), influencing the drone’s heading.
- Speed: Generally controlled indirectly through the responsiveness of the control sticks; faster movements result in higher speed.
Basic Aerial Maneuvers
Performing basic aerial maneuvers requires practice and coordination.
- Turns: Use the right stick to tilt the drone and initiate a turn.
- Ascents: Increase the throttle to raise the drone’s altitude.
- Descents: Decrease the throttle to lower the drone’s altitude.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers and Features

Beyond basic operation, drones offer advanced flight modes and features that enhance capabilities and allow for more complex maneuvers. This section delves into these capabilities and their applications.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS data for position holding and autonomous flight, providing greater stability and ease of use.
- Attitude Mode: Relies on the drone’s internal sensors for stabilization, allowing for more agile maneuvers but requiring more pilot skill.
Advanced Drone Functions
Advanced functions significantly enhance the drone’s capabilities.
- Waypoint Navigation: Allows pre-programming a flight path, enabling autonomous flights along a defined route.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point, providing a safety net in case of signal loss or low battery.
Filming Smooth and Stable Aerial Footage
Capturing high-quality footage requires understanding camera settings and flight techniques.
- Smooth movements: Avoid jerky movements to prevent shaky footage.
- Proper framing: Compose shots carefully to create visually appealing results.
- Appropriate camera settings: Adjust settings like shutter speed and ISO to optimize image quality.
Flight Plan for a Specific Scenario
Let’s consider a scenario: filming a landscape. A flight plan might involve using waypoint navigation to fly along a pre-determined path, capturing various angles and perspectives of the landscape. This might include smooth, slow pans across the scene, and changes in altitude to emphasize specific features.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Safe and responsible drone operation is crucial to prevent accidents and injuries. This section emphasizes safety best practices and legal considerations.
Best Practices for Safe Drone Operation
Always prioritize safety when operating a drone.
- Never fly near people or crowds.
- Maintain visual line of sight.
- Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions.
- Regularly inspect your drone for damage.
- Always have a backup battery.
Legal Requirements and Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location. It is crucial to research and understand the specific laws and regulations in your area before flying.
These regulations often include restrictions on airspace, flight altitudes, and required certifications.
Maintaining a Safe Distance
Always maintain a safe distance from people, property, and obstacles to prevent accidents.
This distance may vary depending on local regulations and the specific circumstances.
Emergency Procedures
In case of a drone malfunction, having a plan in place is crucial.
- Attempt to regain control.
- If control is lost, activate the Return-to-Home (RTH) function (if available).
- If the drone is unresponsive, attempt to land it safely.
- Report any incidents to the relevant authorities.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring reliable performance. This section Artikels key maintenance tasks and common problems.
Routine Drone Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance prevents problems and extends the drone’s operational life.
- Inspect the drone for damage after each flight.
- Clean the propellers and body regularly to remove dirt and debris.
- Store the drone in a cool, dry place.
- Inspect and clean the camera lens regularly.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Several common problems can occur with drones, but many are easily resolved.
- Low battery: Charge the battery.
- Poor signal: Check the distance and ensure clear line of sight.
- Propeller damage: Replace damaged propellers.
- GPS issues: Recalibrate the GPS.
Safe Storage and Transportation
Proper storage and transportation protect your drone from damage.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of safety protocols and regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all these elements, including detailed instructions and helpful tips, please refer to this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will ensure you’re well-prepared to operate your drone responsibly and effectively.
- Use a protective case during transportation.
- Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Store batteries separately and safely.
Replacing or Repairing Damaged Components
Replacing or repairing damaged components may require specialized tools and knowledge. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions or seek professional assistance if needed.
Always use genuine replacement parts to ensure compatibility and safety.
Drone Photography and Videography: How To Operate A Drone
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding the relationship between camera settings and image quality. This section explores techniques and tips for achieving professional results.
Camera Settings and Image Quality
Camera settings significantly impact image quality. Understanding these settings allows for precise control over the final image.
Techniques for Capturing High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
Several techniques can help improve the quality of aerial photos and videos.
- Use a tripod or gimbal for stable shots.
- Plan your shots carefully to ensure good composition.
- Adjust your camera settings based on the lighting conditions.
- Use a ND filter to reduce the amount of light entering the lens.
Tips for Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Composition plays a vital role in creating visually appealing aerial imagery.
- Use leading lines to guide the viewer’s eye.
- Include a strong subject in your shots.
- Use the rule of thirds to create balanced compositions.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
Visual Guide to Camera Settings
Understanding the effect of different camera settings is crucial for optimal results.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the lens. A wider aperture (lower f-number) creates a shallower depth of field, blurring the background. A narrower aperture (higher f-number) increases depth of field, keeping both foreground and background in focus.
- Shutter Speed: Controls how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. A faster shutter speed freezes motion, while a slower shutter speed creates motion blur. Adjust based on the desired effect and lighting conditions.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity of the camera’s sensor to light. A lower ISO reduces noise, but requires more light. A higher ISO is useful in low-light conditions, but increases noise.
Mastering drone operation involves a blend of technical understanding and responsible practice. This guide has equipped you with the foundational knowledge to confidently handle your drone, from pre-flight preparations to executing advanced maneuvers. Remember that safety and legal compliance are paramount. By adhering to best practices and continuously refining your skills, you can unlock the full potential of your drone, capturing stunning aerial footage and exploring new heights with confidence and responsibility.
Safe flying!
FAQ Insights
What is the best drone for beginners?
Several user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring features like GPS stabilization and automated return-to-home functions. Research models with positive reviews and consider your budget.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, battery size, and flight conditions (wind, payload). Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that automatically brings the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight.
Do I need a license to fly a drone?
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, responsible and skillful drone operation ensures both safety and enjoyable flights.
Drone regulations vary by location. Check with your local aviation authority to determine licensing requirements and any airspace restrictions before flying.
